Obesity Rates In The World 2023
Obesity is no longer just a personal health issue — it’s a growing global epidemic. Across the world, countries are reporting alarming increases in obesity rates, with some nations reaching record-breaking levels. According to international health reports, Mexico is now among the countries with the highest obesity rates, raising concern about long-term public health consequences.
Understanding which are the most obese countries in the world, and why, is essential to addressing this challenge. Obesity is driven by multiple factors — from genetics and lifestyle, to economic and cultural habits — making it one of the most complex health problems of our time.
Federation (2019), the fundamental reasons for overweight and obesity are as follows:
The root causes of obesity and overweight are complex and multifactorial. According to the World Obesity Federation (2019), they include:
-
Genetic factors
-
Metabolic and hormonal influences
-
Environmental conditions
-
Psychological and emotional stress
-
Socioeconomic status
-
Unhealthy eating habits
-
Lack of physical activity
-
Poor sleep quality
-
Alcohol consumption
-
Side effects from medications
Since 1975, obesity rates by country have significantly increased. The World Health Organization (2017) reports that over 1.9 billion adults worldwide are overweight, and more than 650 million are obese. This means 39% of the adult population struggles with excess body fat. In most parts of the world, obesity now causes more deaths than being underweight. Fortunately, this is a preventable and manageable condition when addressed early.
What are obesity and overweight?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and the National Center for Health Statistics, obesity is defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health. The most widely used measure to classify obesity rates by country and individual health risk is the Body Mass Index (BMI).
The BMI is a simple calculation based on a person’s height and weight. It is used globally to assess overweight and obesity in adults:
-
Overweight: BMI ≥ 25
-
Obesity: BMI ≥ 30
These thresholds are standardized by the WHO and offer a consistent tool to compare obesity rates across populations. While BMI is useful due to its simplicity and applicability across sexes and ages, it is still a general guideline. It does not distinguish between muscle and fat mass, meaning it may not perfectly reflect body composition in all individuals.
Despite this, BMI remains the most practical metric for monitoring obesity trends and identifying countries with the highest obesity rates in the world.
Obesity and overweight not only affect adults
Obesity and overweight are no longer issues limited to adults or high-income countries. According to 2019 research, an estimated 38.2 million children under the age of 5 worldwide were affected by high obesity rates.
Although these conditions were once considered problems of wealthier nations, recent trends show a significant rise in childhood obesity in low- and middle-income countries, particularly in urban areas. In Africa, for example, the number of overweight children under 5 has increased by nearly 24% since 2000. Additionally, in 2019, almost half of the world’s overweight or obese children under 5 lived in Asia.
Globally, obesity and overweight are now associated with more deaths than underweight, largely due to the sheer number of people affected. This highlights the importance of addressing obesity not just as a personal health issue but as a global public health challenge.
This article presents the most recent obesity rates by country to raise awareness and encourage action. Below, you’ll find data from the World Obesity Federation, including:
-
A list of the most obese countries by population (2017)
-
Countries with the highest obesity percentages
-
The top nations based on obesity prevalence worldwide
The Top Obesity Rates
The Story of Samoa and Tonga: Obesity Rates and Health Challenges
Samoa and Tonga are confronting a pressing health crisis with alarmingly high rates of obesity. In Samoa, 60.8% of men are reported as obese, while Tonga sees an obesity rate of 82.8% among women. These staggering figures underscore the shift from traditional diets to processed foods, sedentary lifestyles, and socio-economic challenges.
This epidemic reflects global trends, with the United States leading in absolute numbers. It’s crucial to comprehend the root causes and ramifications of obesity in these nations, emphasizing the urgent need for effective public health strategies worldwide.
Join the call to action for comprehensive solutions to combat this critical issue and promote global well-being for generations to come.
| Aspect | Obesity in Samoa | Normal Body Type |
|---|---|---|
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | Typically BMI ≥ 30 | BMI within 18.5 – 24.9 |
| Physical Appearance | Larger body size, excess fat distribution | Balanced muscle, fat, and bone distribution |
| Health Risks | Higher risk of diabetes, cardiovascular diseases | Lower risk of obesity-related health issues |
| Implications | Increased healthcare burden, reduced quality of life | Enhanced physical performance, better overall health |
| Intervention Efforts | Health education, lifestyle changes, healthcare support | Health promotion, active lifestyle encouragement |
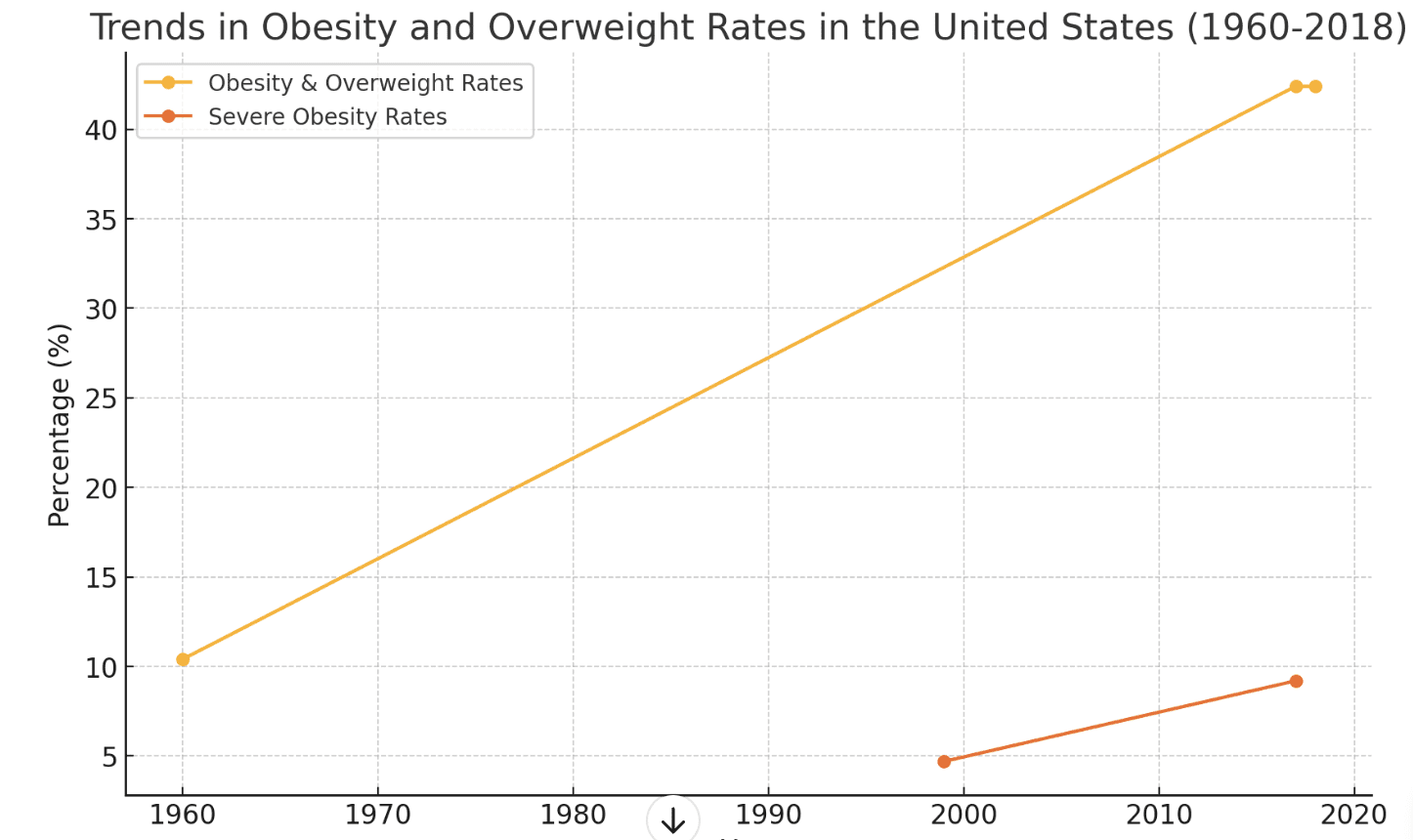
The United States has witnessed a dramatic rise in obesity rates over the decades. In 1960, only 10.4% of the population was considered obese. By 2018, that number had surged to 42.4%. This trend highlights a major public health challenge and positions the U.S. among the countries with the highest obesity rates in the world. Notably, severe obesity has also increased—rising from 4.7% to 9.2%—reflecting deeper concerns beyond general overweight statistics.
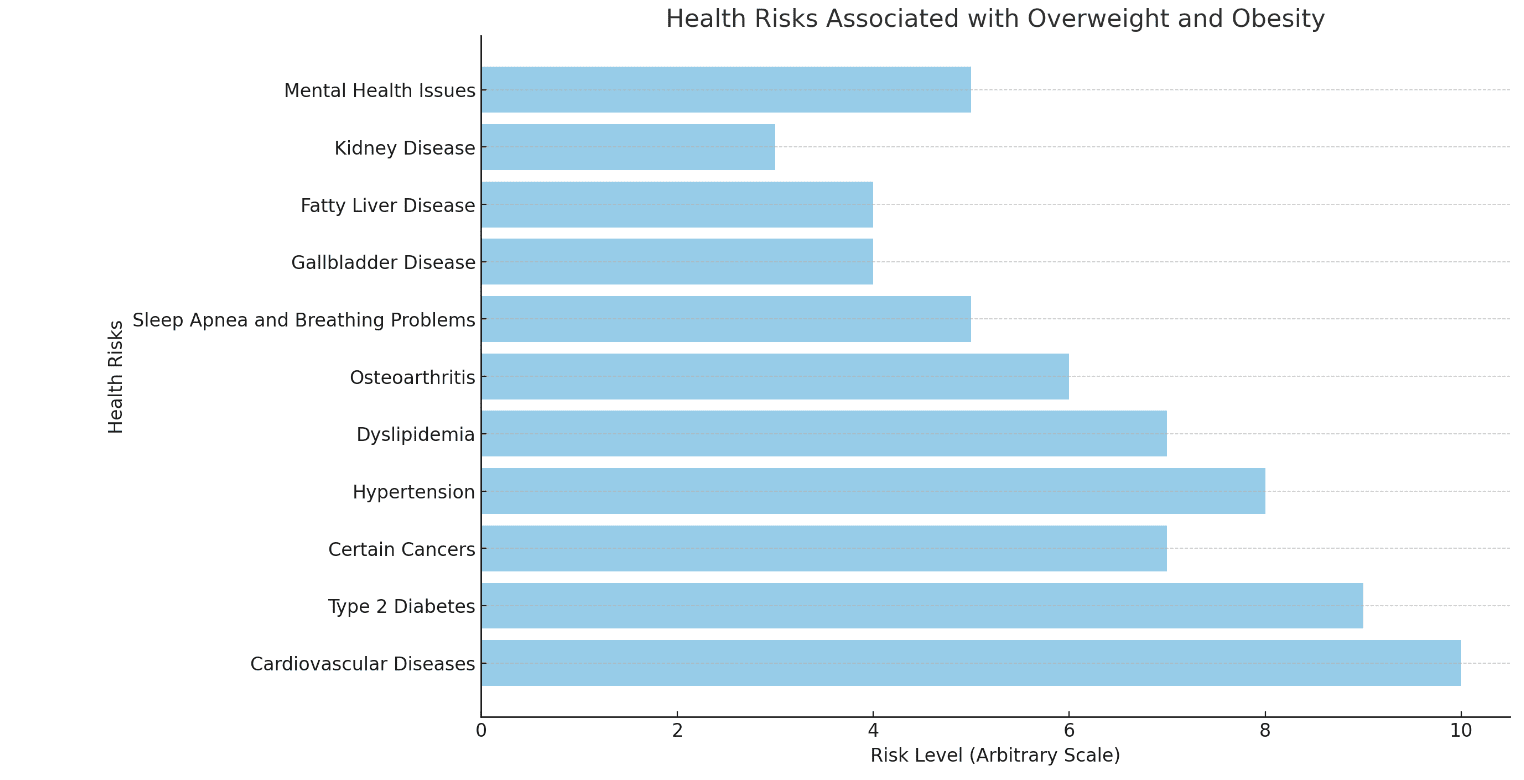
The health consequences of obesity extend far beyond appearance or body weight. As the chart shows, obesity and overweight significantly increase the risk of developing serious medical conditions. These include cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and even certain types of cancer. The length of each bar in the chart represents the relative health risk, emphasizing the importance of prevention and early intervention to reduce the global burden of obesity.
Top 10 countries with the highest Diabetes Rates (2023):
- China – 1,444,216,107
- India – 1,393,409,038
- United States – 332,915,073
- Indonesia – 276,361,783
- Pakistan – 225,199,937
- Brazil – 213,993,437
- Nigeria – 211,400,708
- Bangladesh – 166,303,498
- Russia – 145,912,025
- Mexico – 130,262,216
Obesity and COVID-19
By the beginning of 2021, multiple studies had confirmed a heightened demand for medical services among individuals with obesity who contract COVID-19. A higher body mass index (BMI) has been linked to an increased likelihood of hospitalization, admission to intensive or critical care, and the need for mechanical ventilation. It also raises the risk of mortality from the illness.
Obesity and Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is significantly impacted by excess weight and obesity. It is estimated that 80-85% of the risk of developing type 2 diabetes is associated with being overweight or obese. Recent research indicates that overweight individuals have a higher likelihood of developing this disease compared to those with a BMI of 22 or lower. Moreover, gaining weight in adulthood also raises the risk of diabetes, even for individuals with a healthy BMI.
Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease
Excess weight is directly connected to heart disease, strokes, and cardiovascular risk factors. As BMI increases, so do blood pressure, cholesterol, triglycerides, blood sugar, and inflammation, which in turn increases the likelihood of experiencing cardiovascular complications such as heart attacks or strokes.
Obesity and Cancer
The text you provided explains the link between obesity and different types of cancer. According to research, there is evidence suggesting that obesity is directly associated with cancers of the esophagus, pancreas, colon and rectum, breast, endometrium, kidney, and gallbladder in both men and women.
Can overweight and obesity be reduced?
Yes, overweight and obesity are preventable conditions. Their rising prevalence underscores the need for community-wide and environmental changes that promote a healthier lifestyle. This includes ensuring access to affordable and nutritious food, as well as safe spaces and time for regular physical activity.
Individuals are more likely to adopt a healthy lifestyle when their environment supports it. Simple yet effective actions include:
- Eating more fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and nuts
- Reducing the intake of saturated fats, added sugars, and highly processed foods
- Engaging in daily physical activity—even moderate exercise helps
However, for these personal choices to be truly effective, societal support is crucial. Governments, schools, employers, and local communities must create conditions that make healthy living the easiest choice, not the hardest. This multi-level approach can help reduce obesity rates worldwide, particularly in countries currently facing the highest obesity rates.
Bariatric Surgery as an alternative for treating obesity
Bariatric surgery, also known as metabolic or weight loss surgery, is a medical procedure frequently recommended for individuals struggling with obesity, especially when other treatments have proven ineffective. This approach not only promotes significant and sustained weight loss, but also helps manage and even reverse many obesity-related health conditions.
Research shows that even a moderate reduction in excess body fat can significantly lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. For those already diagnosed, bariatric surgery can lead to better blood glucose control and reduce dependence on medications.
While it’s not a complete cure, this surgery offers a powerful tool for those who are unable to reach healthy weight goals through lifestyle changes alone. In many cases, bariatric procedures restore metabolic health, improve quality of life, and reduce long-term health risks associated with high obesity rates.
Obesity and Overweight Prevalence
By Geographic Region:
| Region | % Obesity | % Overweight |
|---|---|---|
| North | 15.2% | 25.8% |
| South | 19.3% | 32.1% |
| East | 14.8% | 26.4% |
| West | 16.7% | 29.0% |
By Age Group:
| Age Group | % Obesity | % Overweight |
|---|---|---|
| 0-18 | 10.4% | 20.0% |
| 19-35 | 17.3% | 31.5% |
| 36-50 | 24.1% | 37.8% |
| 51+ | 27.5% | 40.2% |
By Gender:
| Gender | % Obesity | % Overweight |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 16.0% | 28.5% |
| Female | 18.5% | 29.8% |
References
- Diabetes Rates By Country 2021. (2021). World Population Review. https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/diabetes-rates-by-country
- Global Health Observatory. (2019). Global Health Observatory. https://data.worldobesity.org/rankings/
- Obesity and overweight. (2016). World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
- Obesity Prevention Source. (s. f.). Harvard T.H. Chan. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/obesity-prevention-source/obesity-consequences/health-effects/
- Prevalence of obesity among adults. (2016). World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/indicators/indicator-details/GHO/prevalence-of-obesity-among-adults-bmi-=-30-(crude-estimate)-(-)
- World Health Organization. (2021, marzo). COVID-19 and Obesity: The 2021 Atlas. https://www.worldobesityday.org/assets/downloads/COVID-19-and-Obesity-The-2021-Atlas.pdf
Feeling stuck?
- Check Your Bariatric Surgery Eligibility Now!
Ready for a Healthier You? Review Your Bariatric Surgery Case Today!
Take the first step towards a healthier, happier you by reviewing your bariatric surgery case. Fill out our quick and easy Surgical Eligibility Form to see if you’re a candidate for life-changing weight loss surgery. Your journey to better health starts here!
Related Post
Learn how to kickstart your weight loss journey